We track a wide array of emerging technologies: blockchain, bitcoin, lightning network, IoT, Machine Learning, Robotics, many others. We are continually adding new technologies as they begin to emerge. Emerging technologies generally follow a similar adoption curve. The Flashstarts Levels of Technology Adoption (FLOTA) is a simple means of placing technologies on the curve.
The value of FLOTA is that it allows organizations to categorize. track and manage each technology and apply the appropriate level of attention and resources at each stage. This ensures that companies don’t overinvest and risk failure or underinvest and risk falling behind their competitors.
The current state of each technology is best represented on a spider/kiviat chart seen below.
Flashstarts Levels of Technology Adoption
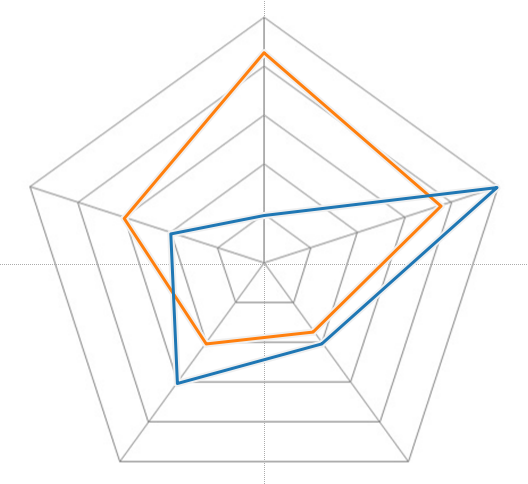
Listed below are the 6 levels of adoption (0-5) with brief descriptions of each.
0 – Unengaged
New technologies are being continuously invented. There is always some period of time before your organization even becomes aware of them. The recommended procedure is to monitor a broad set of information resources keeping an eye out for interesting new technologies. Once located the new technology is placed on your ‘Tracking List’.
1 – Tracking
Tracking involves a periodic (quarterly) review of new technologies at which time they can either be removed from the list, continue being tracked, or bumped to the educational level. The list of formally tracked technologies must be broadly circulated, enabling anyone to contribute or subscribe to the information flow. Criteria include the level of importance, the existence of viable use cases, availability of educational resources, and potential impact on your business.
2 – Educational
Once a new technology is promoted to educational, corporate funds are released to allow employees to learn more about it. Executives can attend seminars and IT developers can participate in training programs and spend time learning new skills. Procedures should be in place that encourage broad internal redistribution of the newly gained knowledge is widely distributed. Individuals and groups may then submit project proposals for pilot projects.
3 – Experimental
Once the first pilot project is approved the new technology is in the experimental phase. Each pilot project should include explicit goals and funding should be strictly time-bound. (This 90-day project is to determine feasibility of….) This minimizes the infinite incubation cash sink problem. The focus should be on lessons learned with minimal focus on success or failure. A formal ‘Lessons Learned’ report should be formally distributed throughout the organization.
4 – Tactical
If a successful pilot is promoted to operational, the deployed new technology passes into the Tactical Level of adoption. At this juncture, standard operating procedures, best practices, security, auditing, and other general corporate governance practices need to be systematically applied.
5 – Strategic
If the deployment of a new technology threatens your underlying business or provides you with a strategic competitive advantage it is deemed strategic. At this point, the technology should be the focus of C-level executives and should involve Corporate Board oversight.


